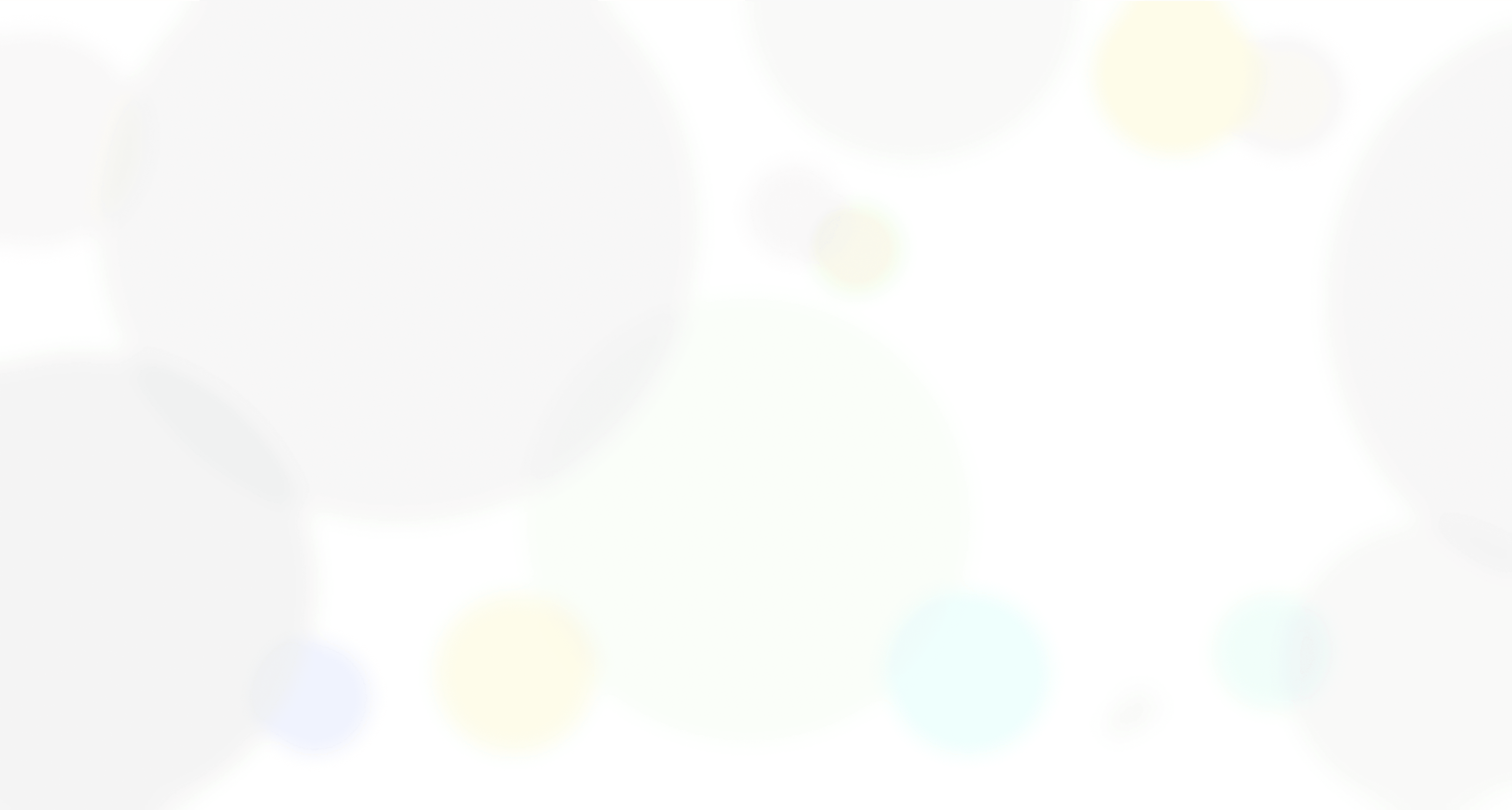Use of Gen AI in Pharmacy Research
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing technology, particularly with generative AI chatbots for academic research. This case study examines their strengths, applications, and areas for improvement to enhance their potential.
Duration
11 Weeks
Timeline
Jan 24 - Apr 24
Role
UX Researcher
Project
Academic
What I did
User Research, User Interviews, Affinity Mapping, Secondary Research, Research Synthesis, Hypothesis
Task brief provided by our professor
Task
Our project began with a brief from our professor, challenging us to understand how generative AI (Gen AI) can be utilized and leveraged for academic research.
Challenge
Our challenge was to explore the current state of Gen AI in academia, understand how students and professors use it, identify barriers, and recommend practical solutions.
Targeted Audience

Selecting the Targeted Audience
Identifying our target audience was a crucial first step in our research. Given the sensitivity of the topic for students and professors, it was essential to determine which groups would be more accessible and willing to share their AI usage experiences. To do this, we conducted an exercise to pinpoint the subjects that could provide us with valuable insights into AI usage.
Pharmacy students in TJU ( Targeted audience)
We decided to focus our research on pharmaceutical students from Thomas Jefferson University as our target audience. With this in mind, we began our study, concentrating on their specific needs and challenges

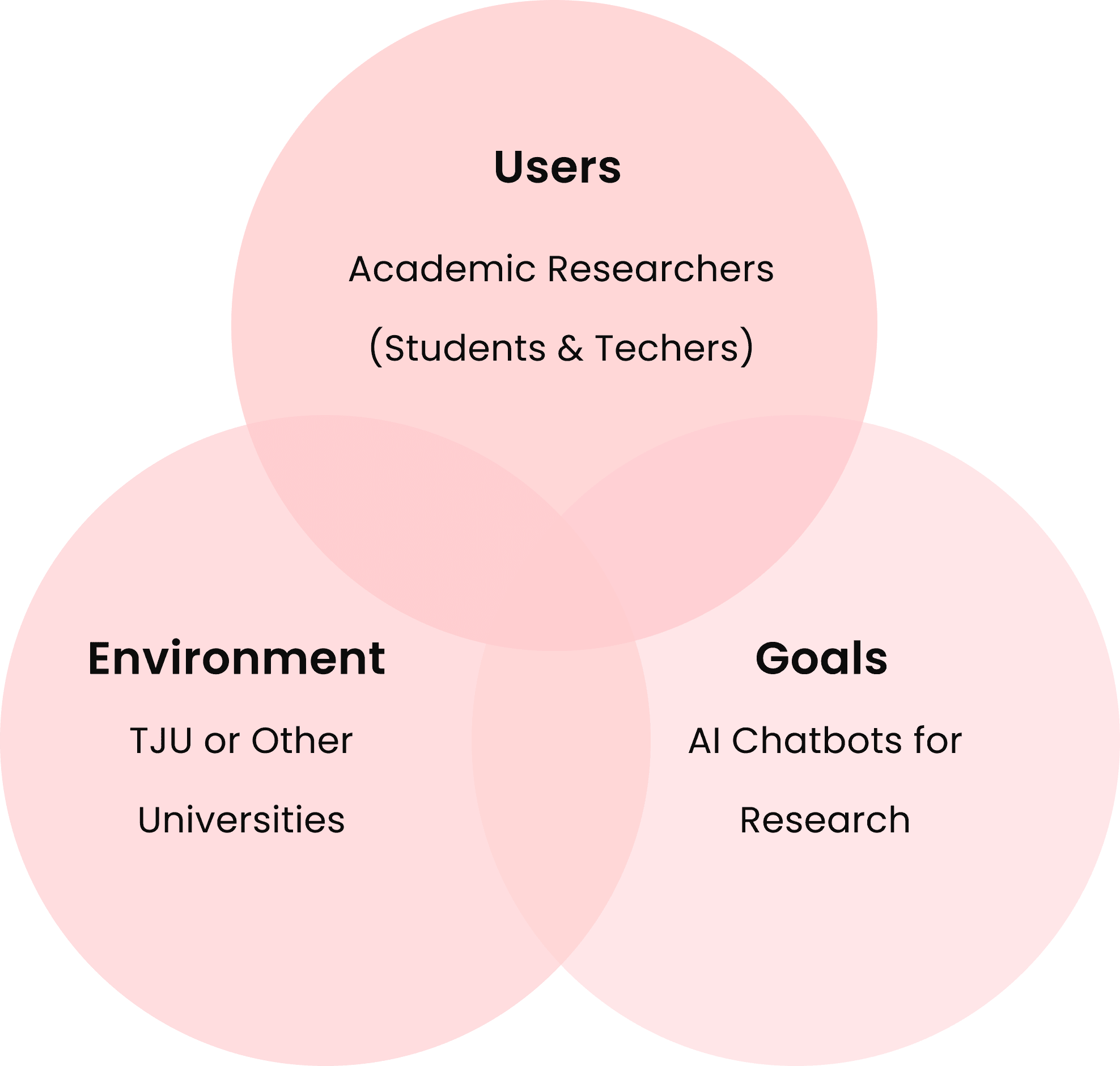
The Users, The Task and The Enviornment
We began by creating a Venn diagram to pinpoint where our goals, target audience, and environment intersected in order to clarify our objectives and focus our research on the key areas of overlap.
As a result, we determined that:
Our task was to conduct in-depth research on AI chatbots.
The users of the AI chatbots would be the pharmacy students.
The environment was Thomas Jefferson University
Goal
Our goal was to learn about generative AI and explore how it can be integrated into Thomas Jefferson University to assist pharmacy students in their research process.
OBJECTIVES
Understand how TJU pharmacy students use generative AI (Gen AI), identifying its advantages and challenges.
Research existing Gen AI sources to assess their benefits and limitations.
Synthesize this data to understand the problem comprehensively and recommend solutions to effectively integrate Gen AI as a research assistant for TJU students.

Research
Exploration of Existing AI Chat Bots useful to Students
Our initial step was to research existing AI tools used by students and professionals for academic and professional tasks. Through our desk research, we identified several widely-used AI tools, particularly popular among students.
Why
To understand the current role of generative AI in pharmacy and research, and to determine the purposes it serves for its users.
User Interview
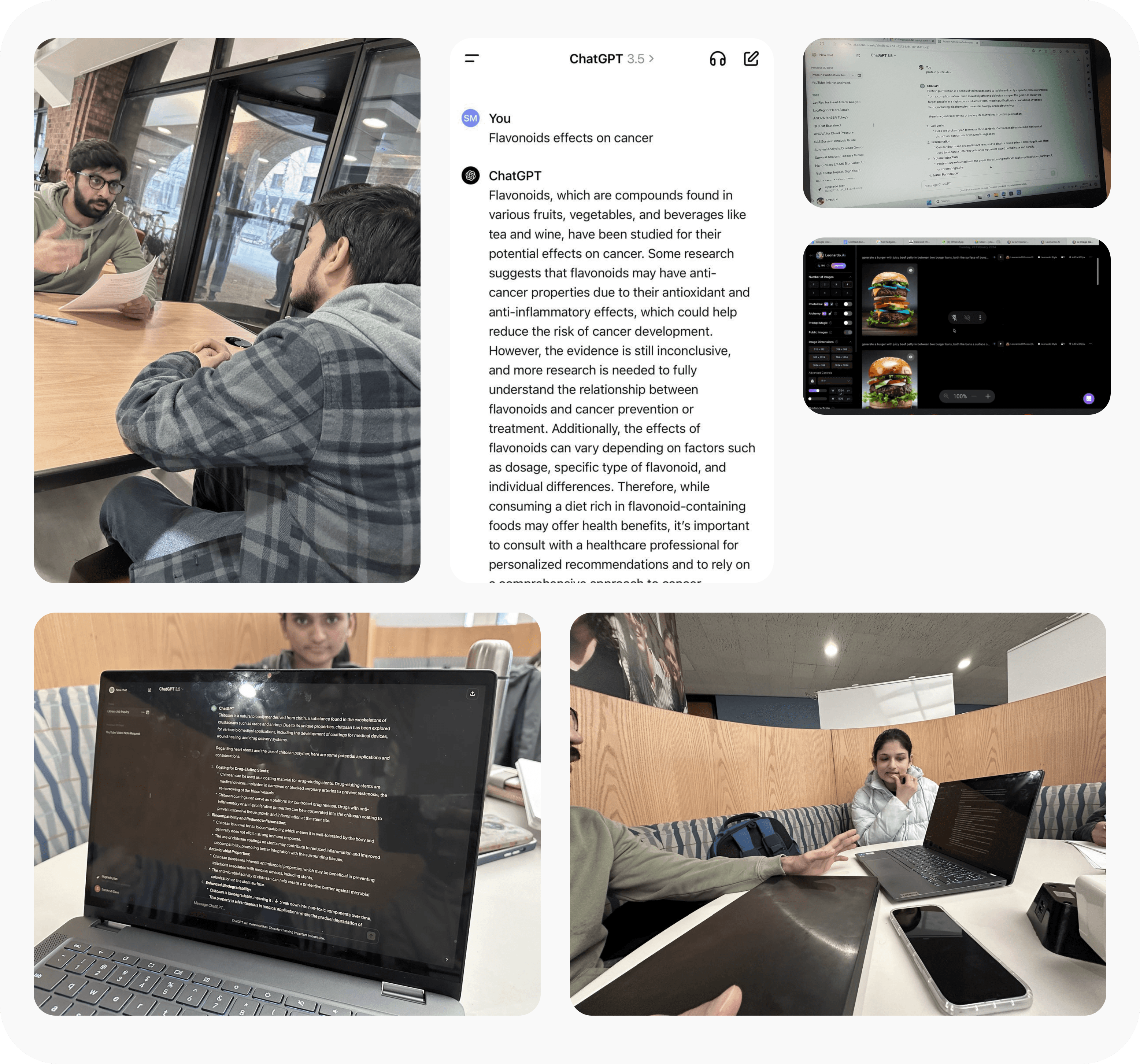
To better understand whether pharmacy students are using generative AI for academic research, and if so, what their experiences have been, we conducted 12 interviews with pharmacy students.
Interview Objectives
Our objective for these interviews was to gain contextual insights into the research practices of pharmacy students, understand their perspectives on the use of generative AI, and identify its advantages and pain points.


Research Synthesis
Interview Outcomes
“
So sometimes when I was searching for a hydrogel formulation for the eye for some of my drug, that time I won't be able to get enough information easily
“
Yeah, as I said, the images which I was trying to generate have never been the kind of accurate for me. I mean, no matter how many prompts I've had, reasonably bad quality images. So images has been a hindrance. “
“
It would be helpful if ChatGPT could provide references or citations for the information it generates. That way, I can verify the authenticity of the content.
Debriefing the Interview outcomes
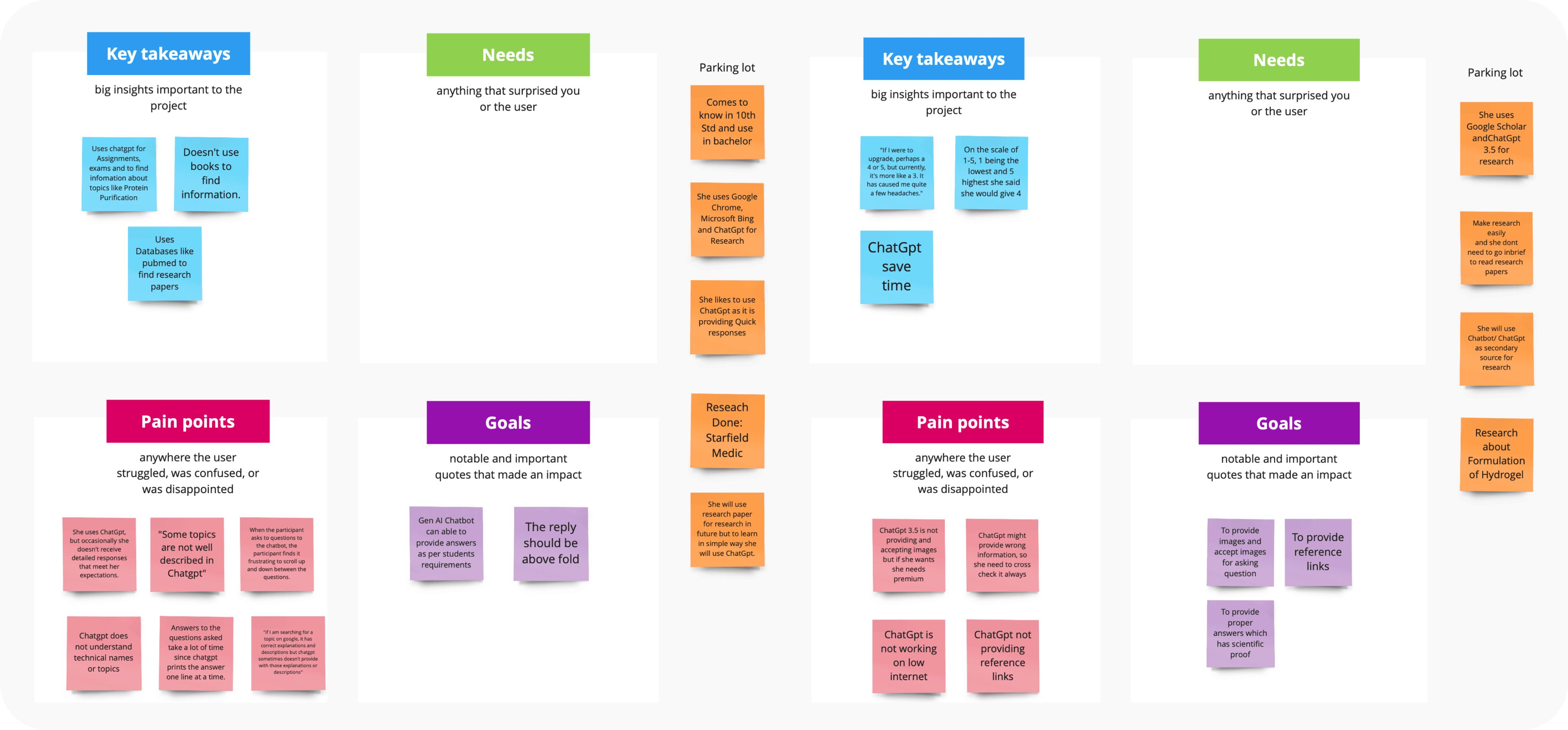
To better understand the pain points and advantages of using Gen AI, we conducted 12 interviews with pharmacy students. Each interview was thoroughly debriefed and systematically organized into individual boards, highlighting the user's benefits, challenges, expectations, and quotes. We then synthesized this information into key takeaways, needs, pain points, and goals, allowing us to identify where problems and advantages overlapped among participants and ultimately guide us toward finding effective solutions.
Problems and Expectations
After debriefing the interviews, we conducted an affinity mapping exercise to categorize the information more efficiently with respect to advantages, pain points, and goals
Pain Points
Lack of references
Inaccurate information
Lack of understanding
Plagiarism check
Privacy concerns
Expectations
Accuracy in information
Source of information
Plagiarism check

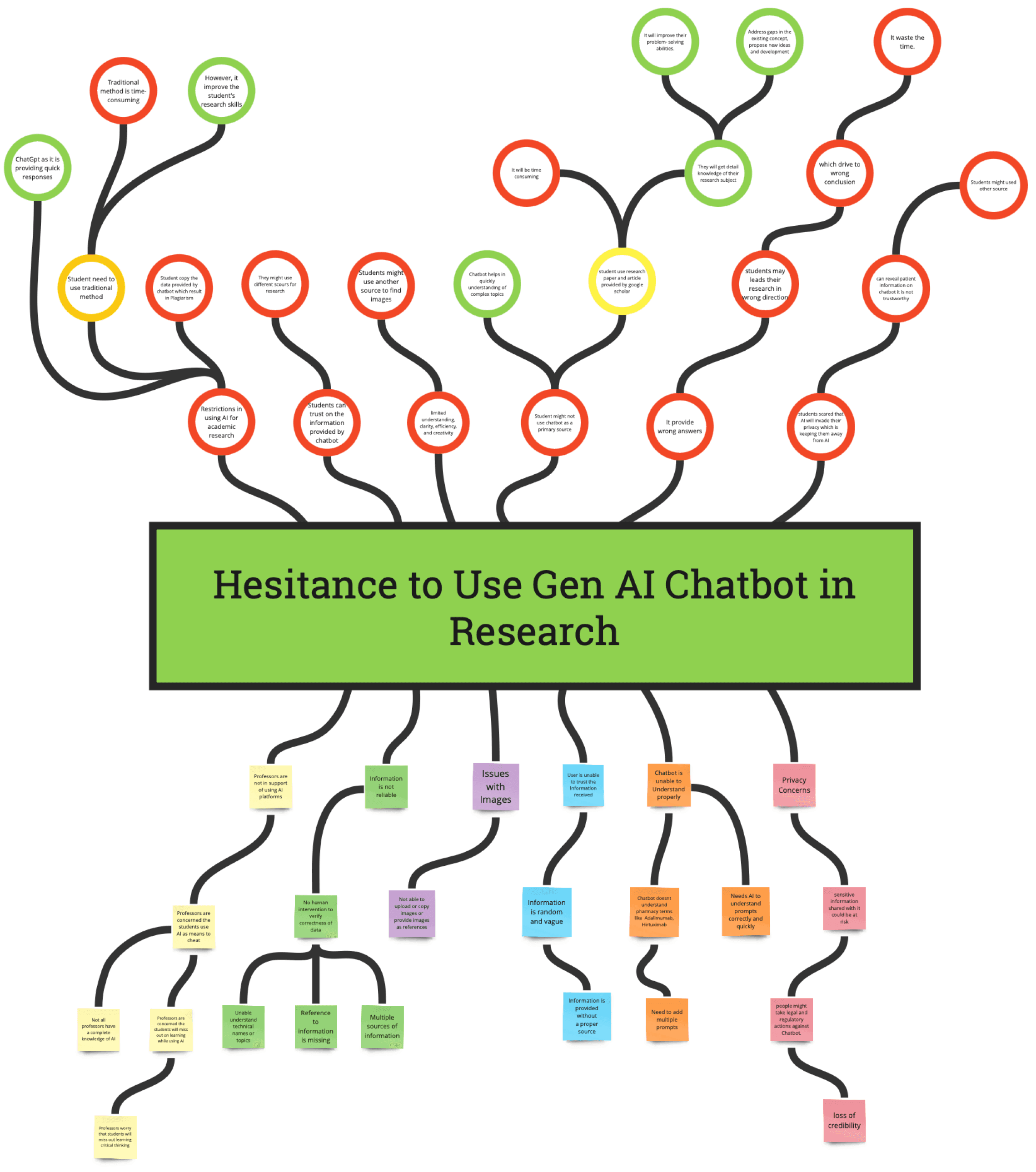
Problem Tree
For our next step, we filtered the data using a problem tree exercise to identify the main recurring problems and their root causes. This process revealed four primary reasons why people do not trust generative AI for their research.
Lack of information
Chatbot does not have access to specific databases
Images
Receiving images as per the prompts is not easy
Missing References
Chatbots do not have the ability to browse the internet or access to external sources
Reliability
Users can not rely on the information provided as it is vague and random
Analyzing the problem
Targeted Problem
After synthesizing our data, we identified the main problems students face and compiled statistics to prioritize them. This analysis helped us determine which issues to address first and find solutions to recommend.

Needs and Expectations
“
I just wish it would just like tell me where like what article is it from if we can pinpoint it to a point where I can just go look at it and try to understand the article as a whole
“
I would like to see chatbots provide information with proper references, especially for complex topics like nanotechnology. Additionally, more detailed information on drugs and their mechanisms of action would be beneficial.
Problem Statement
Pharmacy students encounter challenges using AI in research due to unreliable information lacking proper sources and citations, which undermines the credibility and trustworthiness of the data retrieved for their studies.
How might we
How might we enhance the accuracy of the chatbot data to ensure greater reliability in its responses?
Solution
Ideation
After conducting in-depth research on AI, its current usage, and the problems faced by students, we decided to focus on reliability as the main issue to address. We recommended bridging the traditional research method of using the library with modern AI technology.
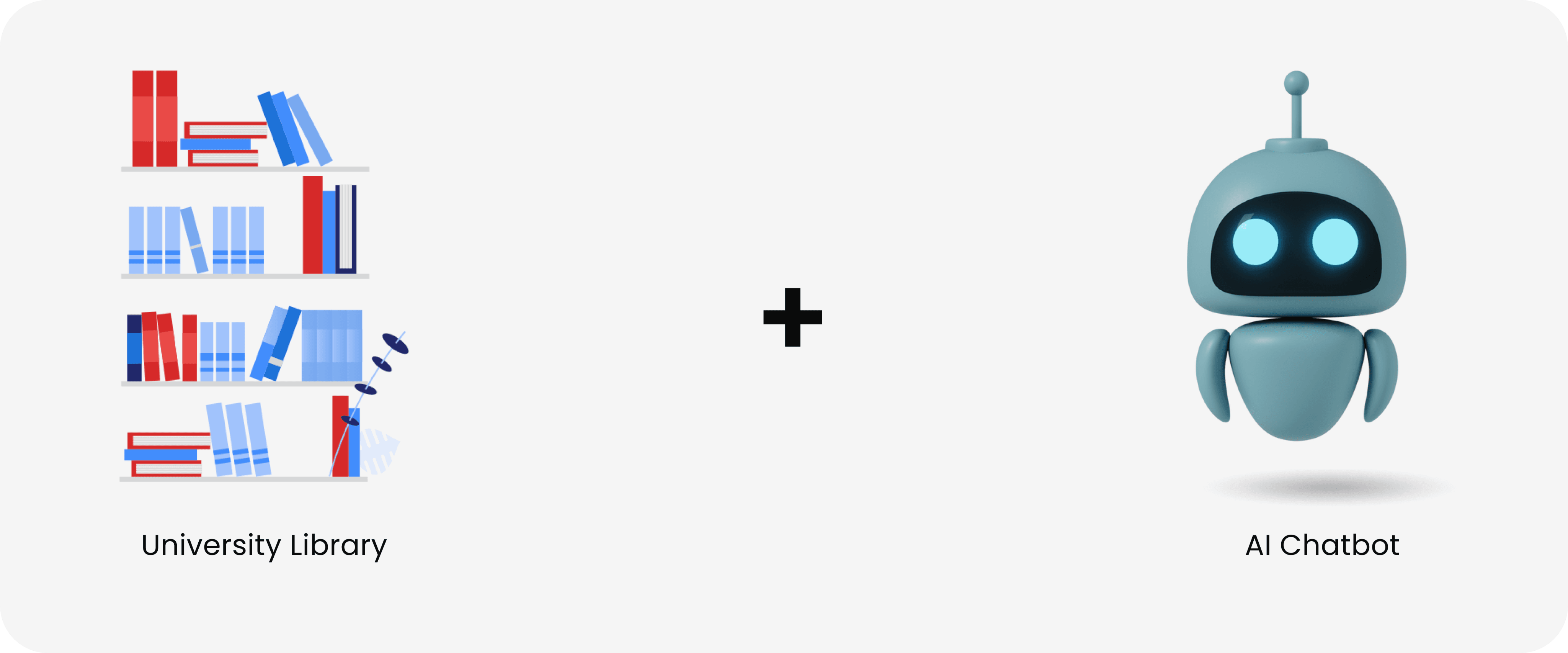
How it works
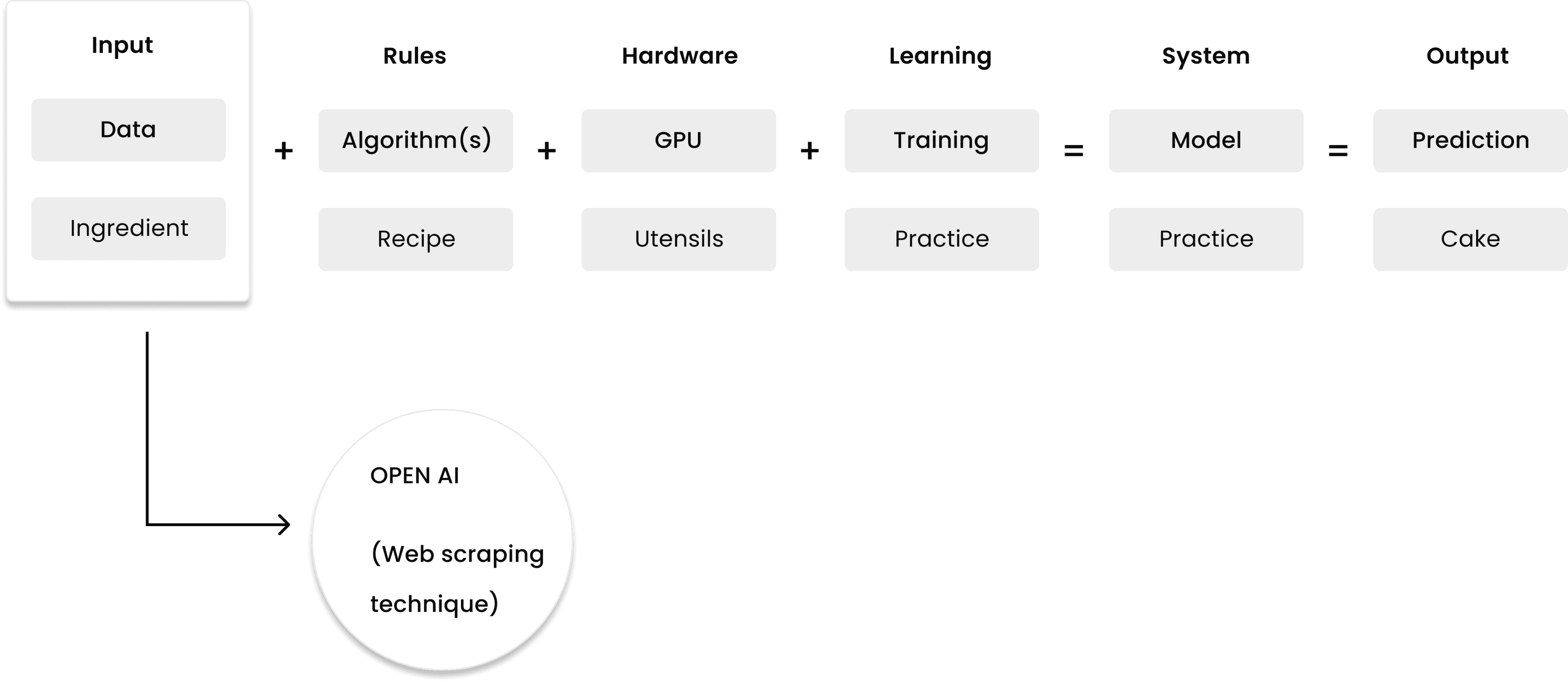
From a recent study in an article we understood that in the current Gen AI models, like ChatGPT, gather their data from OpenAI sources using web scraping techniques.
Existing AI model of Chat GPT
Our recommendation
We recommend using the same generative AI process as ChatGPT, but with an addition: creating an AI chatbot specifically for Thomas Jefferson University. By linking the university's online library as an additional data source, students can receive reliable information directly from a precise search result. This will save students time by eliminating the need to cross-check information.

Benefits
Reliability: Combining traditional research methods with AI ensures more accurate and dependable responses.
Efficiency: Saves time by automating research processes and accessing information swiftly.
Access to Knowledge: Integrates diverse resources to provide comprehensive information retrieval.
User Experience: Smooth interactions enhance overall satisfaction and engagement.
ROI
Cost Savings: Reduces labor hours and increases operational efficiency.
Productivity: Boosts output and academic achievements.
Enhanced Reputation: Demonstrates leadership in innovation and academic excellence.
Long-term Value: Sets the stage for continuous innovation and growth
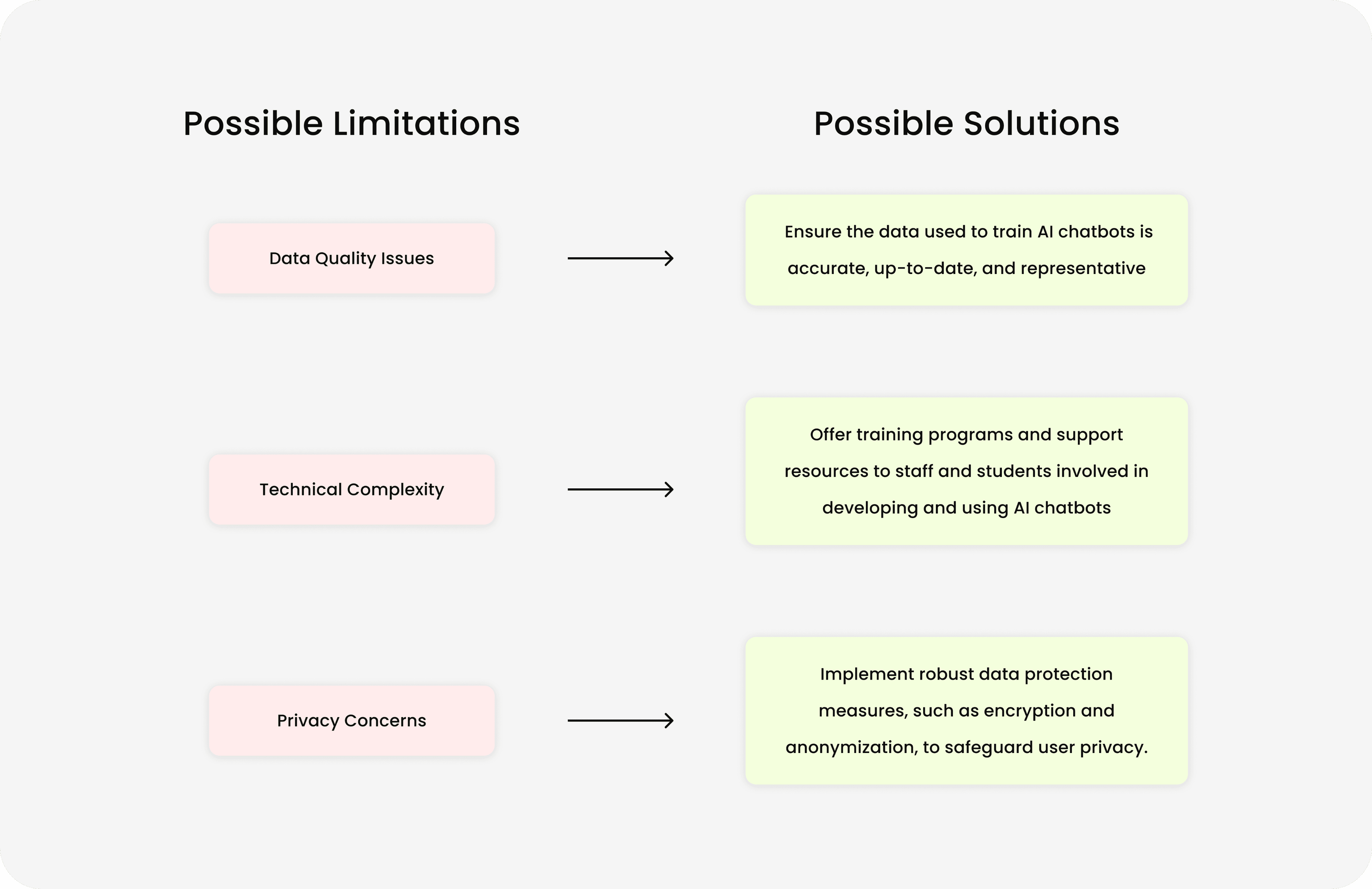
Conclusion
In conclusion, while AI chatbots offer significant benefits such as time-saving and ease of use in pharmacy education research, it is crucial to enhance their reliability in providing accurate responses. Addressing this challenge will maximize the potential of AI chatbots as valuable tools for advancing research and learning in the field.
Other Projects
Hackathon competition
B2C
Mobile Application
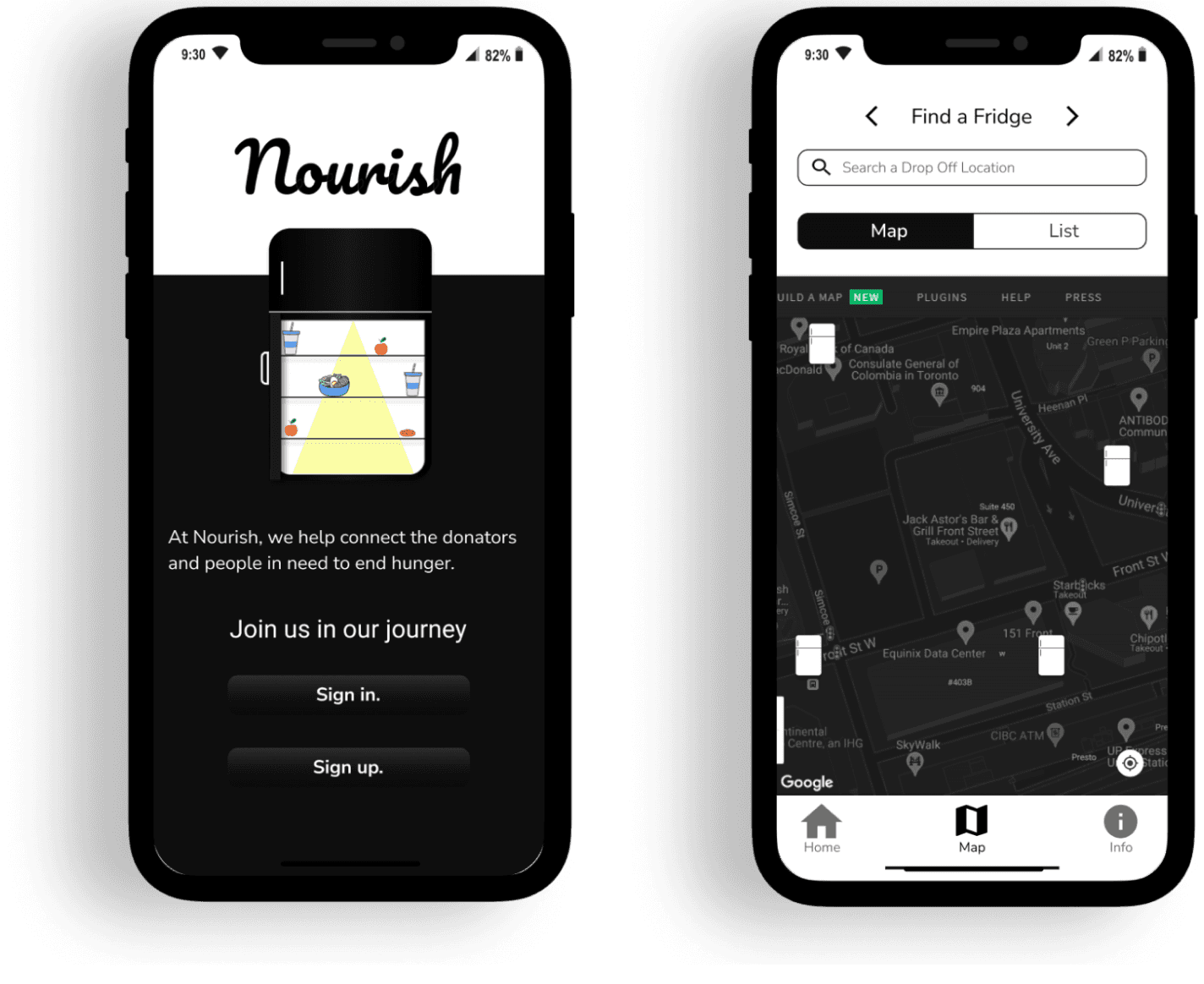
Nourish (Hackathon)
Designed a map-based application to connect people in need of food with those who want to donate.
Academic Project
B2C
Mobile Application
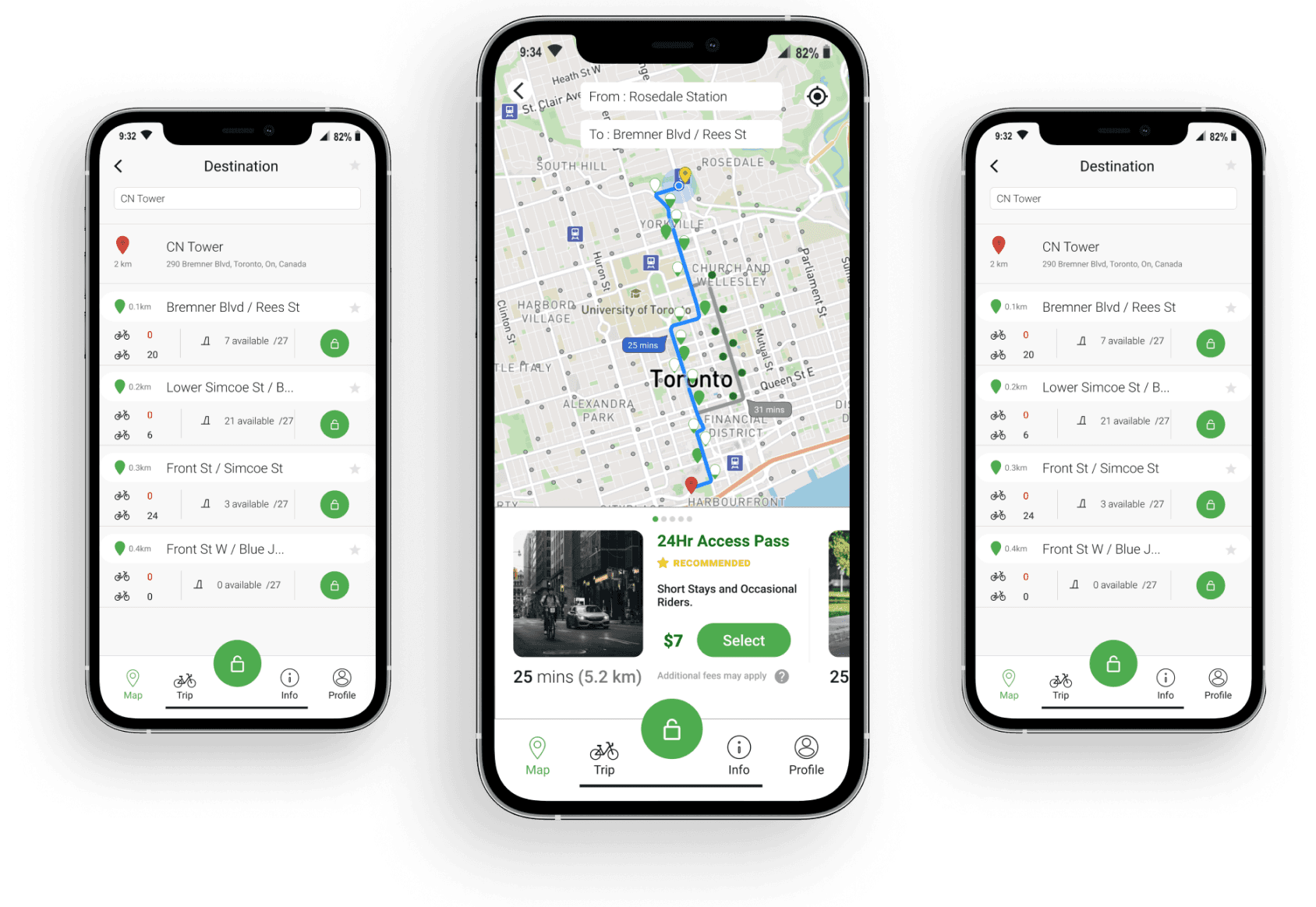
PBSC App (Bike Share)
Redesigned the PBSC application for a better customer experience by implementing new features